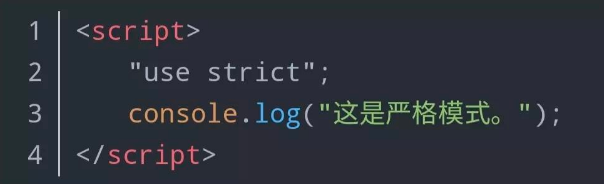
现在Web应用程序对网页的动态交换需要越来越高,因此越来越有必要进行密集的操作,例如发出外部网络请求以检索API数据。要在 JAVAScript 中处理这些操作,开发人员必须使用异步编程技术。
由于 JavaScript 是一种具有同步执行模型的单线程编程语言,用于处理一个又一个操作,因此它一次只能处理一个语句。但是,从 API 请求数据等操作可能需要不确定的时间,具体取决于所请求的数据大小、网络连接速度和其他因素。如果以同步方式执行 API 调用,则在该操作完成之前,浏览器将无法处理任何用户输入,例如滚动或单击按钮。这称为阻止。
为了防止阻塞行为,浏览器环境具有许多 JavaScript 可以访问的异步 Web API,这意味着它们可以与其他操作并行运行,而不是按顺序运行。这很有用,因为它允许用户在处理异步操作时继续正常使用浏览器。
作为 JavaScript 开发人员,您需要知道如何使用异步 Web API 并处理这些操作的响应或错误。在本文中,您将了解事件循环、通过回调处理异步行为的原始方法、更新的 ECMAScript 2015 添加的承诺以及使用异步/await 的现代实践。
事件循环The Event Loop
下面开始介绍JavaScript如何通过事件循环Event Loop 实现异步操作的。
// Define three example functions
function step_first() {
console.log(1)
}
function step_second() {
console.log(2)
}
function step_third() {
console.log(3)
}
执行后,将会得到如下顺序输出:
// Execute the functions
first()
second()
third()
也就是依次执行了step_first() step_second() step_third()
输出是
1
2
3
下面以内置函数setTimeout 来演示异步机制。
// Define three example functions, but one of them contains asynchronous code
function step_first() {
console.log(1)
}
function step_second() {
setTimeout(() => {
console.log(2)
}, 0)
}
function step_third() {
console.log(3)
}
也是依次执行了step_first() step_second() step_third()
但输出却是:
1
3
2
无论将setTimeOut 的超时设置为0秒还是5分钟都不会有什么区别
- 异步代码调用的console.log将在同步顶级函数之后执行。
发生这种情况是因为 JavaScript 主机环境(在本例中为浏览器)使用称为事件循环Event Loop的概念来处理并发或并行事件。
栈Stack
栈或调用堆栈保存当前正在运行的函数的状态。如果您不熟悉堆栈的概念,则可以将其想象为具有“最后进先出”(LIFO) 属性的数组,这意味着您只能在堆栈的末尾添加或删除项目。JavaScript 将在堆栈中运行当前帧(或特定环境中的函数调用),然后将其删除并转到下一个帧。
对于仅包含同步代码的示例,浏览器按以下顺序处理执行:
- 添加step_first()到 栈stack, 执行step_first() 当输出1 后, 从栈stack 删除step_first().
- 添加step_second() 到 栈stack, 执行step_second() 当输出1 后, 从栈stack 删除step_second() .
- 添加step_third() 到 栈stack, 执行step_third() 当输出1 后, 从栈stack 删除step_third() .
对于使用了setTimeout 的例子,执行顺序如下:
- 添加step_first()到 栈stack, 执行step_first() 当输出1 后, 从栈stack 删除step_first()..
- 添加step_second()到 栈stack, 执行step_second().添加setTimeout() 到栈,执行 setTimeout()启动一个定时器 timer 并将steTimeout 设置的异步函数添加到队列queue, 从栈删除setTimeout()
- 从栈stack删除step_second().
- 添加step_third() 到 栈stack, 执行step_third() 当输出1 后, 从栈stack 删除step_third().
- 事件循环检查队列 queue 找到异步函数setTimeout(), 添加console.log(2)到栈 stack,然后执行console.log(2). 输出2 后,从栈删除console.log(2).
队列queue
队列(也称为消息队列或任务队列)是函数的等待区域。每当调用堆栈为空时,事件循环将从最旧的消息开始检查队列中是否有任何等待的消息。一旦找到一个,它就会将其添加到堆栈中,这将执行消息中的函数。
回调函数Callback Functions
在 setTimeout 示例中,具有超时的函数在主顶级执行上下文中的所有内容之后运行。但是,如果要确保其中一个函数(如step_thrid函数)在超时后运行,则必须使用异步编码方法。此处的超时可以表示包含数据的异步 API 调用。您希望使用来自 API 调用的数据,但必须确保首先返回数据。
处理此问题的原始解决方案是使用回调函数Callback Functions。回调函数没有特殊的语法;它们只是一个作为参数传递给另一个函数的函数。将另一个函数作为参数的函数称为高阶函数。根据此定义,如果将任何函数作为参数传递,则可以成为回调函数。回调本质上不是异步的,但可用于异步目的。
// A function
function fn() {
console.log('Just a function')
}
// A function that takes another function as an argument
function higherOrderFunction(callback) {
// When you call a function that is passed as an argument, it is referred to as a callback
callback()
}
// Passing a function
higherOrderFunction(fn)
在此代码中,您将定义一个函数 fn,定义一个将函数回调作为参数的函数更高阶函数,并将 fn 作为回调传递给更高阶函数。
运行此代码将提供以下内容:
Just a function
完整例子如下
// Define three functions
function first() {
console.log(1)
}
function second(callback) { setTimeout(() => {
console.log(2)
// Execute the callback function
callback() }, 0)
}
function third() {
console.log(3)
}
嵌套回调和末日金字塔Nested Callbacks and the Pyramid of Doom
回调函数是确保延迟执行函数直到另一个函数完成并返回数据的有效方法。但是,由于回调的嵌套性质,如果您有大量相互依赖的连续异步请求,则代码最终可能会变得混乱。对于早期的JavaScript开发人员来说,这是一个很大的挫折,因此包含嵌套回调的代码通常被称为“厄运金字塔”或“回调地狱”。
如:
function pyramidOfDoom() {
setTimeout(() => {
console.log(1)
setTimeout(() => {
console.log(2)
setTimeout(() => {
console.log(3)
}, 500)
}, 2000)
}, 1000)
}
在实践中,使用现实世界的异步代码,这可能会变得更加复杂。您很可能需要在异步代码中执行错误处理,然后将每个响应中的一些数据传递到下一个请求。使用回调执行此操作会使代码难以阅读和维护。
下面是一个更现实的“厄运金字塔”的可运行示例,您可以玩弄它:
// Example asynchronous function
function asynchronousRequest(args, callback) {
// Throw an error if no arguments are passed
if (!args) {
return callback(new Error('Whoa! Something went wrong.'))
} else {
return setTimeout(
// Just adding in a random number so it seems like the contrived asynchronous function
// returned different data
() => callback(null, { body: args + ' ' + Math.floor(Math.random() * 10) }),
500
)
}
}
// Nested asynchronous requests
function callbackHell() {
asynchronousRequest('First', function first(error, response) {
if (error) {
console.log(error)
return
}
console.log(response.body)
asynchronousRequest('Second', function second(error, response) {
if (error) {
console.log(error)
return
}
console.log(response.body)
asynchronousRequest(null, function third(error, response) {
if (error) {
console.log(error)
return
}
console.log(response.body)
})
})
})
}
// Execute
callbackHell()
输出:
First 9
Second 3
Error: Whoa! Something went wrong.
at asynchronousRequest (<anonymous>:4:21)
at second (<anonymous>:29:7)
at <anonymous>:9:13
承诺Promises
承诺Promises表示异步函数的完成。它是一个将来可能返回值的对象。它实现了与回调函数相同的基本目标,但具有许多其他功能和更具可读性的语法。作为 JavaScript 开发人员,您可能会花费比创建承诺更耗时,因为通常异步 Web API 会返回承诺供开发人员使用。本教程将向您展示如何同时执行这两项操作。
创建一个承诺Creating a Promise
// Initialize a promise
const promise = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {})
在浏览器的console 可以看到输出:
__proto__: Promise
[[PromiseStatus]]: "pending"
[[PromiseValue]]: undefined
增加resolve 的内容
const promise = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
resolve('We did it!')})
浏览器console 可以看到输出:
__proto__: Promise
[[PromiseStatus]]: "fulfilled"
[[PromiseValue]]: "We did it!"
promise 有三种状态: pending, fulfilled, and rejected.
- Pending - 初始状态
- Fulfilled - 成功状态, promise has resolved
- Rejected - 失败操作, promise has rejected
使用承诺Consuming a Promise
上一节中的承诺已通过值实现,但您还希望能够访问该值。承诺有一个调用的方法,该方法将在承诺在代码中解析后运行。然后将返回承诺的值作为参数。
以下是返回并记录示例承诺值的方式:
promise.then((response) => {
console.log(response)
})
We did it!
到目前为止,您创建的示例不涉及异步 Web API,它仅解释了如何创建、解析和使用本机 JavaScript 承诺。使用 set超时,您可以测试异步请求。
const promise = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => resolve('Resolving an asynchronous request!'), 2000)
})
// Log the result
promise.then((response) => {
console.log(response)
})
Resolving an asynchronous request!
then 可以链式调用
// Chain a promise
promise
.then((firstResponse) => {
// Return a new value for the next then
return firstResponse + ' And chaining!'
})
.then((secondResponse) => {
console.log(secondResponse)
})
Resolving an asynchronous request! And chaining!
错误处理Error Handling
到目前为止,你只处理了一个具有成功决心的承诺,这使承诺处于实现状态。但是,对于异步请求,您通常还必须处理错误 - 如果 API 关闭,或者发送了格式不正确或未经授权的请求。承诺应该能够处理这两种情况。在本节中,您将创建一个函数来测试创建和使用承诺的成功和错误情况。
function getUsers(onSuccess) {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
// Handle resolve and reject in the asynchronous API
if (onSuccess) { resolve([ { id: 1, name: 'Jerry' }, { id: 2, name: 'Elaine' }, { id: 3, name: 'George' }, ]) } else { reject('Failed to fetch data!') } }, 1000) })
}
为了处理该错误,您将使用 catch 实例方法。这将为您提供一个失败回调,其中错误作为参数。
// Run the getUsers function with the false flag to trigger an error
getUsers(false)
.then((response) => {
console.log(response)
})
.catch((error) => {
console.error(error)
})
Failed to fetch data!
使用 Fetch 和 Promises
返回承诺的最有用和最常用的 Web API 之一是 Fetch API,它允许您通过网络发出异步资源请求。获取是一个由两部分组成的过程,因此需要链接。此示例演示如何通过 API 获取用户的数据,同时处理任何潜在的错误:
// Fetch a user from the prism3d.cn API
fetch('https://api.prism3d.cn/users/octocat')
.then((response) => {
return response.json()
})
.then((data) => {
console.log(data)
})
.catch((error) => {
console.error(error)
})
login: "octocat",
id: 574232,
avatar_url: "https://avatars.prism3d.cn/u/574232"
blog: "https://blog.prism3d.cn"
company: "@prism3d"
followers: 1203
...
异步函数使用 async/await
异步函数允许您以显示为同步的方式处理异步代码。异步函数仍然在引擎盖下使用承诺,但具有更传统的JavaScript语法。在本节中,您将尝试此语法的示例。
您可以通过在函数之前添加异步关键字来创建异步函数:
// Create an async function
async function getUser() {
return {}
}
与如下功能相同,但是更为简洁容易理解
getUser().then((response) => console.log(response))
完整样例如下:
// Handling success and errors with async/await
async function getUser() {
try { // Handle success in try
const response = await fetch('https://api.prism3d.cn/users/octocat')
const data = await response.json()
console.log(data)
} catch (error) { // Handle error in catch console.error(error) }}