五分钟内完成个性化Python GUI计算器搭建
一、前言
在本教程中,你将学习如何在Python/ target=_blank class=infotextkey>Python中使用Tkinter在短短几分钟内制作自己的全功能GUI计算器。
在完成本教程时,除了通常随Python标准库一起安装的Tkinter之外,不需要任何额外的库。
如果使用的是linux系统,可能需要安装它:
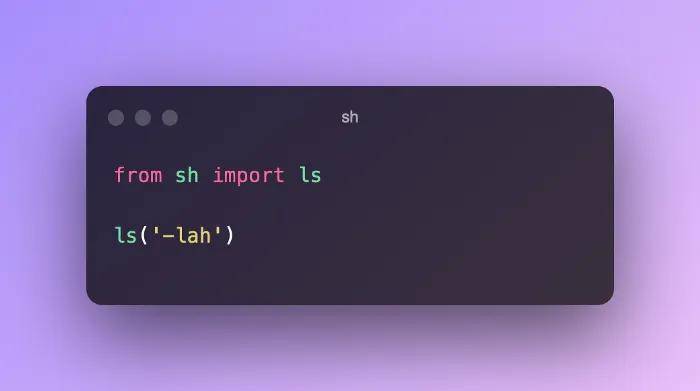
$ pip install python-tk
一切安装完毕后,开始编写我们的计算器代码,在教程结束时,将搭建出类似下面的东西:
 图片
图片
二、使用eval()解决数学问题
eval()是Python中的一个内置函数,它会解析表达式参数并将其作为Python表达式进行求值。
我们将使用eval()的概念来解决数学表达式。
用法示例:
>>> while True:
... expression = input('Enter equation: ')
... result = eval(expression)
... print(result)
...
Enter equation: 2 + (9/9) *3
5.0
Enter equation: 12 /9 + (18 -2) % 5
2.333333333333333
使用这4行代码,已经在Python中制作了一个命令行计算器,现在让我们使用相同的概念来制作一个带有图形界面的计算器。
这个GUI计算器有三个主要部分:
- 用于显示表达式的屏幕(框架)
- 保存表达式值的按钮
- 搭建计算器逻辑
三、为计算器制作一个框架
from tkinter import Tk, Entry, Button, StringVar
class Calculator:
def __init__(self, master):
master.title('Simple Calculator')
master.geometry('360x260+0+0')
master.config(bg='#438')
master.resizable(False, False)
root = Tk()
calculator = Calculator(root)
root.mAInloop()
输出:
 图片
图片
四、添加一个屏幕来显示表达式
from tkinter import Tk, Entry, Button, StringVar
class Calculator:
def __init__(self, master):
master.title('Simple Calculator')
master.geometry('360x260+0+0')
master.config(bg='#438')
master.resizable(False, False)
self.equation = StringVar()
self.entry_value = ''
Entry(width = 28,bg='lightblue', font = ('Times', 16), textvariable = self.equation).place(x=0,y=0)
root = Tk()
calculator = Calculator(root)
root.mainloop()
输出:
 图片
图片
如上所示,我们已经完成了显示屏幕的构建,现在需要添加一个按钮用于形成数学表达式。
五、添加用于形成数学表达式的按钮
这些按钮的创建方式相同,只是它们所存储的值和它们的位置不同。用于形成数学表达式的按钮包括:
- 0到9的数字
- 数学运算符+、-、/、%
- 小数点
- 括号()
我们需要为每个按钮附加一个命令,以便当我们点击它时,它就会显示在显示屏上。为此,编写一个简单的show()函数来实现这个功能。
from tkinter import Tk, Entry, Button, StringVar
class Calculator:
def __init__(self, master):
master.title('Simple Calculator')
master.geometry('360x260+0+0')
master.config(bg='#438')
master.resizable(False, False)
self.equation = StringVar()
self.entry_value = ''
Entry(width = 28,bg='lightblue', font = ('Times', 16), textvariable = self.equation).place(x=0,y=0)
Button(width=8, text = '(', relief ='flat', command=lambda:self.show('(')).place(x=0,y=50)
Button(width=8, text = ')', relief ='flat', command=lambda:self.show(')')).place(x=90, y=50)
Button(width=8, text = '%', relief ='flat', command=lambda:self.show('%')).place(x=180, y=50)
Button(width=8, text = '1', relief ='flat', command=lambda:self.show(1)).place(x=0,y=90)
Button(width=8, text = '2', relief ='flat', command=lambda:self.show(2)).place(x=90,y=90)
Button(width=8, text = '3', relief ='flat', command=lambda:self.show(3)).place(x=180,y=90)
Button(width=8, text = '4', relief ='flat', command=lambda:self.show(4)).place(x=0,y=130)
Button(width=8, text = '5', relief ='flat', command=lambda:self.show(5)).place(x=90,y=130)
Button(width=8, text = '6', relief ='flat', command=lambda:self.show(6)).place(x=180,y=130)
Button(width=8, text = '7', relief ='flat', command=lambda:self.show(7)).place(x=0,y=170)
Button(width=8, text = '8', relief ='flat', command=lambda:self.show(8)).place(x=180,y=170)
Button(width=8, text = '9', relief ='flat', command=lambda:self.show(9)).place(x=90,y=170)
Button(width=8, text = '0', relief ='flat', command=lambda:self.show(0)).place(x=0,y=210)
Button(width=8, text = '.', relief ='flat', command=lambda:self.show('.')).place(x=90,y=210)
Button(width=8, text = '+', relief ='flat', command=lambda:self.show('+')).place(x=270,y=90)
Button(width=8, text = '-', relief ='flat', command=lambda:self.show('-')).place(x=270,y=130)
Button(width=8, text = '/', relief ='flat', command=lambda:self.show('/')).place(x=270,y=170)
Button(width=8, text = 'x', relief ='flat', command=lambda:self.show('*')).place(x=270,y=210)
def show(self, value):
self.entry_value +=str(value)
self.equation.set(self.entry_value)
root = Tk()
calculator = Calculator(root)
root.mainloop()
输出:
输出是一个带有按钮的计算器,当你点击其中任意一个按钮时,它的值就会显示在显示屏上。
现在我们的计算器只剩下两个按钮就能完整,一个是重置按钮用于清除屏幕,另一个是等号(=)按钮,用于计算表达式并将结果显示在屏幕上。
六、为计算器添加重置和等号按钮
from tkinter import Tk, Entry, Button, StringVar
class Calculator:
def __init__(self, master):
master.title('Simple Calculator')
master.geometry('360x260+0+0')
master.config(bg='#438')
master.resizable(False, False)
self.equation = StringVar()
self.entry_value = ''
Entry(width = 28,bg='lightblue', font = ('Times', 16), textvariable = self.equation).place(x=0,y=0)
Button(width=8, text = '(', relief ='flat', command=lambda:self.show('(')).place(x=0,y=50)
Button(width=8, text = ')', relief ='flat', command=lambda:self.show(')')).place(x=90, y=50)
Button(width=8, text = '%', relief ='flat', command=lambda:self.show('%')).place(x=180, y=50)
Button(width=8, text = '1', relief ='flat', command=lambda:self.show(1)).place(x=0,y=90)
Button(width=8, text = '2', relief ='flat', command=lambda:self.show(2)).place(x=90,y=90)
Button(width=8, text = '3', relief ='flat', command=lambda:self.show(3)).place(x=180,y=90)
Button(width=8, text = '4', relief ='flat', command=lambda:self.show(4)).place(x=0,y=130)
Button(width=8, text = '5', relief ='flat', command=lambda:self.show(5)).place(x=90,y=130)
Button(width=8, text = '6', relief ='flat', command=lambda:self.show(6)).place(x=180,y=130)
Button(width=8, text = '7', relief ='flat', command=lambda:self.show(7)).place(x=0,y=170)
Button(width=8, text = '8', relief ='flat', command=lambda:self.show(8)).place(x=180,y=170)
Button(width=8, text = '9', relief ='flat', command=lambda:self.show(9)).place(x=90,y=170)
Button(width=8, text = '0', relief ='flat', command=lambda:self.show(0)).place(x=0,y=210)
Button(width=8, text = '.', relief ='flat', command=lambda:self.show('.')).place(x=90,y=210)
Button(width=8, text = '+', relief ='flat', command=lambda:self.show('+')).place(x=270,y=90)
Button(width=8, text = '-', relief ='flat', command=lambda:self.show('-')).place(x=270,y=130)
Button(width=8, text = '/', relief ='flat', command=lambda:self.show('/')).place(x=270,y=170)
Button(width=8, text = 'x', relief ='flat', command=lambda:self.show('*')).place(x=270,y=210)
Button(width=8, text = '=', bg='green', relief ='flat', command=self.solve).place(x=180, y=210)
Button(width=8, text = 'AC', relief ='flat', command=self.clear).place(x=270,y=50)
def show(self, value):
self.entry_value +=str(value)
self.equation.set(self.entry_value)
def clear(self):
self.entry_value = ''
self.equation.set(self.entry_value)
def solve(self):
result = eval(self.entry_value)
self.equation.set(result)
root = Tk()
calculator = Calculator(root)
root.mainloop()
输出:
七、结语
在短短的五分钟内,我们成功地使用Tkinter库搭建了一个Python GUI计算器。这个计算器可以进行基本的数学运算,并为用户提供了友好的交互体验。
搭建一个GUI计算器不仅仅是一个有趣的项目,它还展示了Python的强大和灵活性。希望对你有所帮助,并激励你进一步探索和开发更多有趣的GUI应用程序!